On August 2, Volvo Cars announced the global auto sales data. The data shows that in July this year, Volvo Cars’ global sales volume was 57,447 vehicles, an increase of 6% year-on-year; among them, the sales volume of new energy vehicles (including pure electric models and plug-in hybrid models) was 27,879 vehicles, accounting for 48.53% of the total sales volume, and the sales volume of pure electric models was 14,130 vehicles. From January to July this year, Volvo Cars’ global total sales volume was 445,520 vehicles, an increase of 13% year-on-year.

Specifically looking at its models, the model with the highest sales volume of Volvo Cars in July was Volvo XC60, with 15,577 vehicles; XC40/EX40 and EX30 followed, with sales volumes of 13,818 vehicles and 9,201 vehicles respectively. In response to the growth in global sales in July, Volvo Cars officials said that the growth in global sales was mainly due to the increase in the sales volume of electric models in the European market.
When细分 into various major markets, Volvo Cars’ sales volume in the European market in July was 28,390 vehicles, an increase of 40% year-on-year, among which the sales volume of new energy vehicles was 18,482 vehicles, an increase of 64% year-on-year, accounting for 65.10% of the total European auto sales volume in July. In addition, the sales volume in the US market was 9,597 vehicles, a decrease of 11% year-on-year, but the sales volume of plug-in hybrid models increased significantly by 73% year-on-year to 3,242 vehicles, while the sales volume of pure electric models decreased by 59% year-on-year to 520 vehicles.
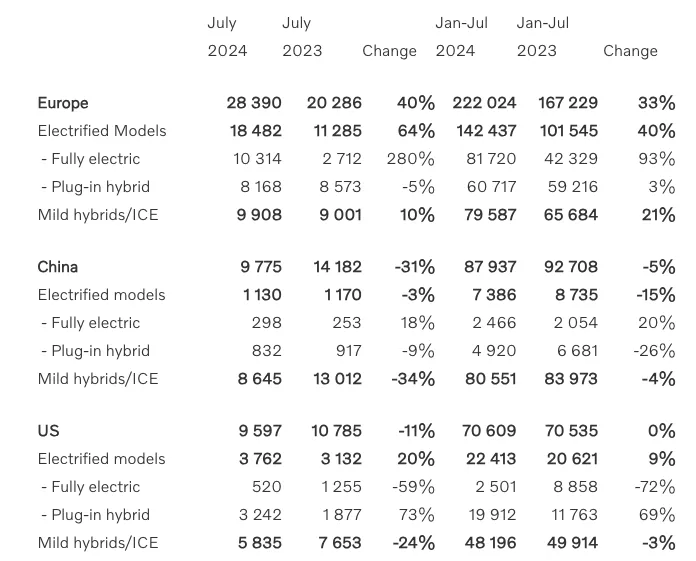

Compared to the European market and the US market, Volvo Cars appears to be very lonely in the Chinese market. In July this year, the sales volume in China was 9,775 vehicles, a decrease of 31% year-on-year. Among them, the sales volume of new energy vehicles was 1,130 vehicles, a decrease of 3% year-on-year; the sales volume of pure electric models was 298 vehicles, an increase of 18% year-on-year. When extending the time to the first seven months of this year, Volvo’s sales volume in China was also in a downward trend, a decrease of 5% to 87,937 vehicles. Among them, the sales volume of new energy vehicles was 7,386 vehicles, a decrease of 15%.
The main reason for the poor sales performance of Volvo in China is the lack of highlights in new energy models. Up to now, the models that Volvo has achieved domestic production in China include four models of S90, S60, XC60, and XC40. Among them, S90, S60, and XC60 have launched plug-in hybrid models on the basis of fuel vehicles, and XC40 has launched a pure electric model on the basis of fuel vehicles. Analyzing from the retail data, in the first half of this year, the model with the highest sales volume of Volvo Cars in China was XC60, with a cumulative sales volume of 32,600 vehicles; S90 and S60 followed, with 16,500 vehicles and 9,100 vehicles respectively; XC40 was 4,500 vehicles.

And the sales volume of pure electric new energy vehicles in the first half of the year was only a few hundred vehicles, among which the sales volume of XC40 new energy was 246 vehicles; EX30 was 199 vehicles; C40 was 125 vehicles; EM90 was 107 vehicles, which was far from the mainstream new energy models in the auto market.

In the middle of last month, Volvo Cars officials announced that due to uncertainties in the macro economy and geopolitics, it will lower the annual sales forecast. Volvo Cars said that if there is no major interference, the sales target will increase by 12% to 15%. Before that, Volvo Cars set the annual sales target as an increase of 15%, that is to say, the annual sales growth rate of Volvo Cars has been lowered from the original increase of 15% to an increase of 12% to 15%. Official data shows that from January to July this year, Volvo Cars’ global total sales volume was 445,520 vehicles, an increase of 13% year-on-year.

Analyzing from the global market sales volume of Volvo Cars, whether it is the July sales volume or the cumulative sales volume in the first seven months, the global sales performance of Volvo Cars is still worthy of recognition, but it is not satisfactory when looking at the sales volume in the Chinese market. It should be faced squarely that China has now become the largest new energy vehicle market in the world. Under this background, Volvo Cars has also made quite a lot of changes to the Chinese market.
In August and December 2023, Volvo Cars had “changed the helm” in China several times. On August 18 of that year, Martin Persson, the current general manager of Volvo Cars Japan, returned to China and served as the general manager of the sales company in Greater China; on December 11, Volvo again announced that Yu Kexin, the current vice president of the sales company in Greater China of Volvo Cars, would take up the post of acting president of the sales company in Greater China.

In addition to the personnel aspect, on September 19 of the same year, Volvo Cars also announced with great fanfare that it will stop the production of diesel vehicles at the beginning of 2024 and plans to become a pure electric vehicle brand by 2030 and a climate-neutral company by 2040.
As a Nordic luxury brand, Volvo has indeed made a lot of efforts in realizing the electric transformation, and even directly issued the determination of “stopping the research and development and manufacturing of internal combustion engines and fully transforming to electrification in the future” in the early stage. But as a result, the achievements obtained by Volvo are not obvious, especially in the Chinese market. We believe that the reason for the poor sales volume of Volvo in China is related to the fact that most of the new energy vehicles currently sold are “fuel-to-electric” products, which is also the key reason why it is difficult to increase the sales volume.
How to accelerate the transformation and development and deal with the attack of Chinese independent brands” has become an urgent issue for Volvo to solve in China. In terms of new energy products, Volvo urgently needs to make up lessons.