According to media reports, Mitsubishi Motors will join the alliance of Honda and Nissan. It is understood that the three companies plan to standardize the in-vehicle software of controlled cars. It is expected that Nissan and Honda will jointly develop the basic software and will discuss the application on Mitsubishi Motors. At the same time, the three companies will also consider complementing each other’s model lineups.
Facing the complexity of the global automotive market and the cooling of electric vehicle demand, Honda and Nissan consider cooperating to overcome these challenges, seek to share R & D costs, accelerate the innovation of electric vehicle technology, and use economies of scale to reduce costs to deal with the competitive pressure of the global market more effectively. In March this year, Nissan and Honda announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding to carry out comprehensive cooperation in the electric vehicle business, including joint procurement, joint development of power platforms, and generalization of spare parts. Nissan and Honda hope to achieve cost reduction through resource integration and enhance the product competitiveness of Chinese electric vehicles.

Once the news was announced, it immediately triggered heated discussions. The slow electrification transformation of Japanese automakers has become an inherent perception in the industry. And currently, Japanese automakers have increasingly felt the pressure from the market, especially in the Chinese market, where they need to face the competition with self-owned brands such as BYD, Geely, Changan, and Chery.
In the field of fuel vehicles, Nissan and Honda still have a stable position, but under the background of the accelerated global new energy transformation, the competition in electric vehicles is becoming increasingly fierce. The slow electrification transformation of Nissan and Honda, especially the sluggish performance in the pure electric vehicle business, makes them feel more and more passive.
Industry insiders believe that this cooperation can be regarded as抱团 for warmth among large automotive manufacturers under the tide of electrification. Honda and Nissan are the second and third largest automotive manufacturers in Japan, while Mitsubishi Motors ranks fifth. Judging from the disclosed information, the cooperation among the three auto companies is to share the R & D and procurement costs of the electric vehicle business, so as to make the “plate” of the electric vehicle business larger, and thereby promote the further optimization of the Japanese automotive supply chain. However, the cooperation among the three auto companies is not close, because they only signed a cooperation agreement, and there is a possibility of dissolution in the future after their respective electric vehicle businesses have achieved certain progress.

The electrification transformation requires long-term huge capital investment. By finding partners and sharing the R & D costs through the scale effect, there are also many precedents in the industry, such as Audi and SAIC, Volkswagen and XPeng, and Stellantis Group and Leapmotor. The same is true for the cooperation among Nissan, Honda, and Mitsubishi. They will continue to explore in the pure electric route, but at the same time, they also face relatively large challenges.
In the Chinese market, as new energy vehicles continue to squeeze the market share of fuel vehicles, the market share of Japanese vehicles in the past three years has been 22.6%, 20.0%, and 17.0% respectively, and the market share has continued to shrink. In 2023, the sales of Toyota, Honda, and Nissan in China decreased by 1.7%, 10.1%, and 16.1% respectively. In the first half of the year, the market share of Japanese brands in the Chinese market dropped to 14.9%.
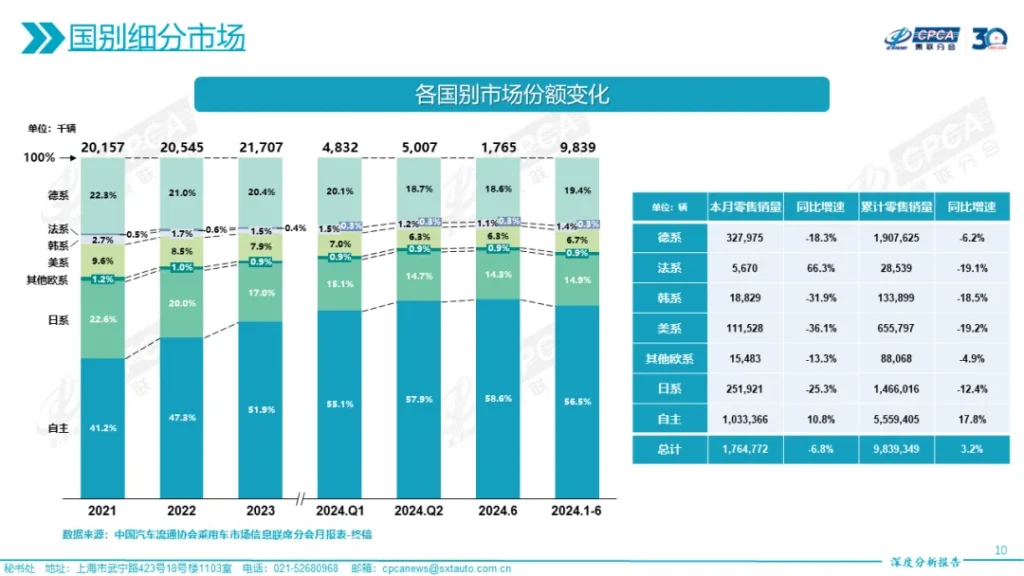
In the overseas market, Japanese automakers also feel the pressure from Chinese automakers. In 2023, China surpassed Japan to become the world’s largest auto exporter. And in the Southeast Asian market where Japanese vehicles have a strong advantage, Chinese automakers have already exerted certain pressure on Japanese vehicles with the electric vehicle business.
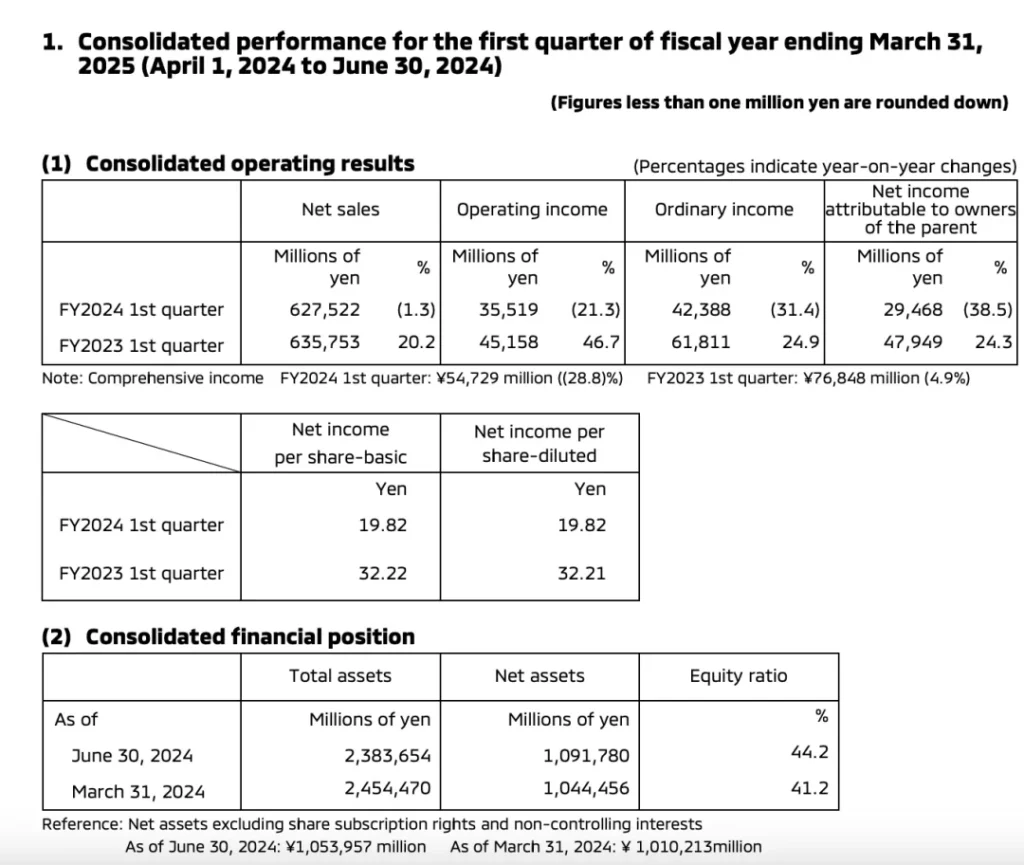
Recently, Mitsubishi Motors released a report stating that in the second quarter, Mitsubishi Motors’ operating profit decreased by 21.3% year-on-year to 35.519 billion yen, and its net profit decreased by 38.5% year-on-year to 193 million US dollars, and its revenue decreased by 1.3% year-on-year to 41.15 billion US dollars. From a regional perspective, the North American region accounted for the largest share in Mitsubishi’s global operating profit in the second quarter, which was 136 million US dollars, accounting for 58% of the total operating profit. In contrast, the operating profit in the Southeast Asian region decreased by one-third to 26.8878 million US dollars. Regarding the impairment of performance, Matsuoka Kentaro, Mitsubishi’s vice president and chief financial officer, explained that it was due to reasons such as the deterioration of the business environment and the increase in sales expenses in Southeast Asia, which led to the loss of speed in performance growth.
As globally renowned automotive manufacturers, Nissan, Honda, and Mitsubishi have deep accumulations in technology and capital. With greater determination to jointly move towards the electric vehicle business, whether they will catch up later and have a certain impact on the competition pattern of the global electric vehicle market has attracted attention.